|
Spectrometer Avaspec 2048FI equipped with SONY 2048 detectors based on silicon CCD arrays. 
The Charged Coupled Device (CCD) detector stores the charge, dissipated as photons strike the photoactive surface. At the end of a controlled time-interval (integration time), the remaining charge is transferred to a buffer and then this signal is being transferred to the AD converter. 
CCD detectors have an enormous dynamic range, only limited by the dark (thermal) current and the speed of the AD converter. Advantages for the CCD detector are many pixels (2048), high sensitivity and high speed. Main disadvantage is the lower S/N ratio.

| Detector SONY2048 specification |
| Type |
CCD linear array |
| # Pixels, pitch |
2048,14 mkm |
| pixel width/ height |
14 x 56 mkm |
| Sensitivity |
240 V/lx.s |
| Sensitivity (AvaLight-HAL, 8 um fiber) in counts per ms integration
time |
5000 counts/W |
| Peak wavelength |
500 nm |
| Signal/Noise |
250:1 |
| Dark noise |
Ca. 10 counts |
| PNRU*(max.) |
± 5% |
| Frequency |
2 MHz |
*PNRU (Photo Response Non-Uniformity) - max difference between output of pixels with uniformly illuminated, divided by average signal. |
|
 |

The sensitivity of a detector pixel at a certain wavelength is defined as the detector electrical output per unit of radiation energy (photons) incident to that pixel. 
The relation between light
energy entering the optical bench and the amount hitting a single detector
pixel depends on the optical bench configuration. The efficiency curve of the
grating used, the size of the input fiber or slit, the mirror performance
and the use of a Detector Collection Lens are the main parameters. Cylindrical Detector Collection Lens (DCL) mounted directly on the detector array. 
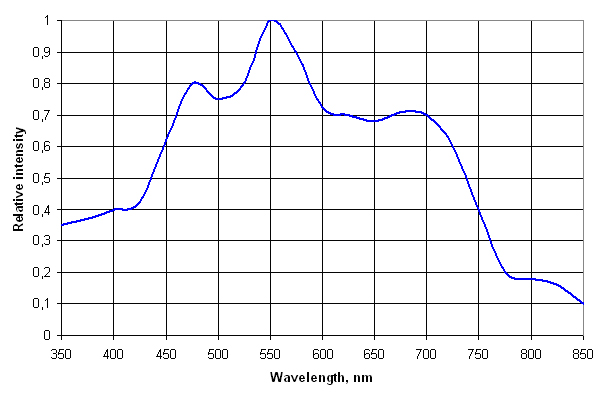 Detector spectral
sensitivity 
|
